Have you noticed that your hlr lookup system is giving you problems just when you need it most? The HLR Lookup service is critical in telecommunications, as it allows you to check if a phone number is active before launching your marketing campaigns or sending critical communications.
When you integrate an hlr lookup service into your systems, you expect it to work accurately and consistently. The reality is that several technical factors can interfere with its performance. HLR verification directly queries the central database of mobile operators to know the current status of any number. This feature helps you focus your SMS marketing campaigns only on numbers that are actually available, generating significant savings.
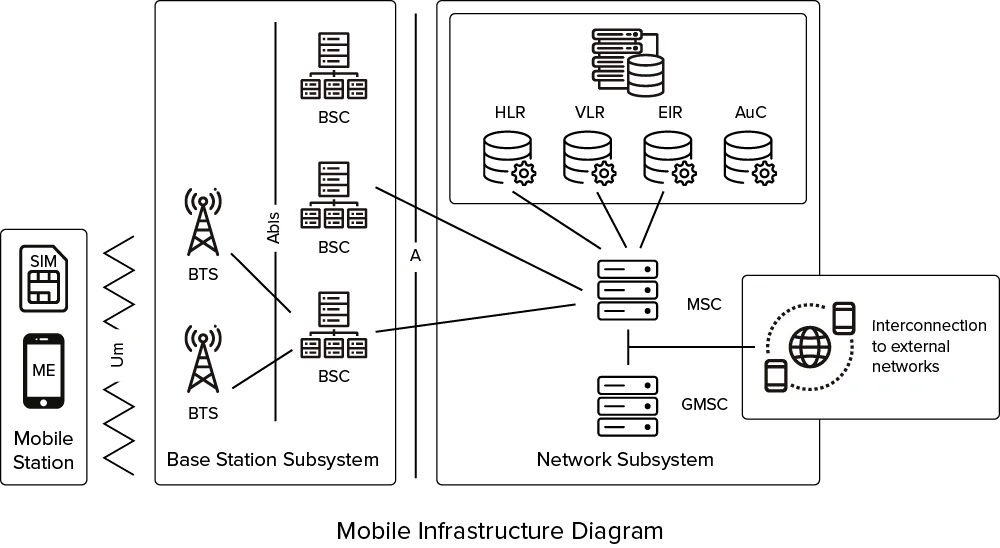
The HLR registry works as a centralized database where each mobile operator stores the essential information of all its users with active SIM cards. In addition, this validation service helps you verify that the numbers stored in your contact databases are still working, considerably reducing the costs of your phone communications and SMS campaigns.
In this article, you’ll learn exactly why HLR checks fail, how to properly read their results, and most valuablely, the technical solutions that actually work to improve your validation rate. We will also see when it is best to consider alternatives to the traditional HLR according to your specific case and we will present the alternative to the HLR Lookup validation of Verificaremails with 100% global coverage where the status of the mobile is checked in real time.
Main Technical Causes of HLR Verification Failures
Image Source: link.springer.com
The effectiveness of your hlr lookup service depends on several technical elements that you should know. If you’re not getting the results you’re hoping for, you’re probably running into one of these main problems.
Formatting errors in international numbers (E.164)
The E.164 standard is crucial for correctly identifying telephone numbers worldwide. The International Telecommunication Union established this international format to ensure that each device has a globally unique number. The most frequent problems you’ll encounter include:
- Missing international prefix (+)
- Added special spaces or symbols
- Keeping the leading zero on certain numbers (as with Scots)
- Exceed the maximum 15 digits allowed
Remember that a valid Spanish number must appear as “+34912345678”, never as “0034 912 34 56 78”. When you make these mistakes, the system can’t establish proper communication with the operators’ databases.
Limited mobile operator coverage
The HLR system does not operate as a single platform, but is distributed among different global mobile operators. Many of these carriers restrict access to the HLR based on specific countries or types of use, which means you don’t have guaranteed coverage for all carriers. This problem is especially intensified in areas with small operators or countries that have technological limitations.
In a world exclusive, Verificaemails has developed a solution to validate phone numbers with worldwide coverage and that offers coverage to countries where HLR verification is not possible. This solution is very useful in the United States, Mexico, Peru, Brazil and the main South American countries where HLR validation does not work.
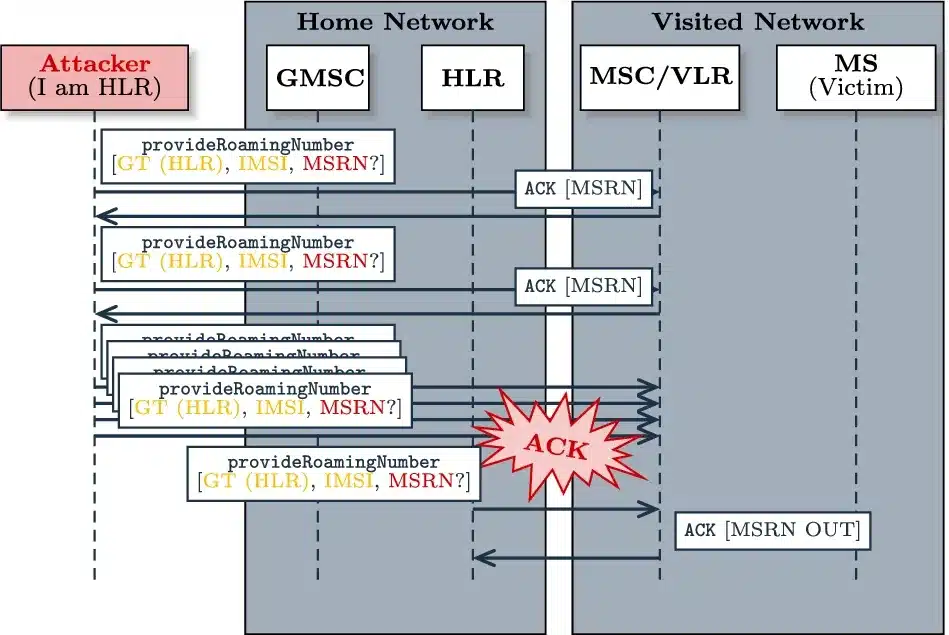
SS7 Network Access Restrictions
HLR queries are generally limited to authorized entities. Reports indicate that more than 80% of telecom operators have faced or detected attacks of some kind. For this reason, operators have implemented strict restrictions on access to SS7 networks to protect their infrastructure, limiting who can perform these checks.
Undetectable virtual or temporary numbers
Virtual and temporary numbers present a particular challenge for HLR verification. As these numbers are not linked to traditional physical SIM cards, they are not always registered in conventional HLR databases, which greatly complicates their validation process.
Front-Lined Issues (MNP)
Mobile number portability allows you to keep your number when you change carriers. However, during this porting process, inconsistencies can be generated in the HLR databases, causing incorrect results or “unknown” states during verifications. While these issues typically resolve over time, they directly affect service reliability.
How to correctly interpret HLR lookup results
Image Source: HLR Lookup
Knowing how to read the results of the HLR lookup correctly will allow you to get the most out of this tool. The data you receive contains valuable information about the availability and specific characteristics of each mobile number you verify.
Meaning of is_reachable, line_type and carrier
Here are the three most important parameters you’ll find in every HLR check:
is_reachable: Tells you if the number is active and can receive communications. The values you’ll typically see are “Active” when the number is working correctly, “Inactive” if the number is unserviced, or “Validating” while the verification process is in progress.
line_type: Identify what type of line you’re checking. You will be able to distinguish between mobile, landline, tollfree, VoIP and other types of telephone services.
carrier: Shows the current carrier of the number. This information is especially useful when you’re working with numbers that have been ported between different companies.
Remember that when the system returns “DELIVERED_TO_HANDSET”, the number is correctly assigned and working. If you see “UNDELIVERABLE_NOT_DELIVERED”, it means that the number is not assigned or has technical problems.
MCC/MNC codes and their relevance
These codes help you pinpoint the mobile network where the number is registered:
MCC (Mobile Country Code): It is a three-digit code that identifies the country. For example, 214 correspond to Spain.
MNC (Mobile Network Code): Identifies the specific carrier within the country. For example, 01 corresponds to Vodafone Spain.
The MCCMNC combination, such as 21401, uniquely identifies each operator worldwide. This information will allow you to optimize the routing of your messages and reduce sending costs.
Cases of ‘unknown’ response and how to act
What to do when you receive an “unknown” response? This result can appear for several reasons:
- The number is in the wrong format
- There are problems during the porting process
- The operator restricts HLR queries
- A temporary error occurred on the mobile network
- There are international routing issues
We recommend that you verify the number format first, try another number from the same carrier, and if possible, retry verification later.
Common mistakes: CALL_BARRED, HLR_ABORT, TELESERVICE_NOT_PROVISIONED
These technical errors need a specific interpretation:
CALL_BARRED: The number has blocked incoming or outgoing calls by user or operator settings.
HLR_ABORT: The HLR record is not responding, indicating a problem in communication with the mobile operator.
TELESERVICE_NOT_PROVISIONED: The SMS service is down or the SIM card is not properly registered on the network.
Do not automatically discard these numbers from your database, as many of these errors are temporary and may be caused by momentary failures on the user’s network or device.
Proven technical solutions to improve validation rate
Image Source: Easy Send SMS
To overcome the technical issues we’ve seen in your HLR validation, there are specific strategies that will improve your results from day one.
Use of multiple HLR lookup providers for greater coverage
We recommend deploying multiple hlr lookup providers working in parallel to greatly increase your validation capacity. Each provider has its strengths in specific regions and carriers. Sempico Solutions, for example, offers worldwide coverage for HLR and MNP searches, with ongoing 24/7/365 support. This redundancy ensures you have consistent responses, even when a provider has time constraints.
Pre-validation of the format with libraries such as libphonenumber
Libphonenumber, the library developed by Google, is your best ally for validating numbers before launching HLR queries. With this tool, you can automatically format phone numbers according to international standards, validate numbers using functions such as isValidNumber() and isPossibleNumber(), and determine the type of number you are processing (mobile, landline, toll-free).
This prevalidation eliminates most E.164 format errors, which as we saw earlier, are the main cause of failures in HLR queries.
Implementing automatic retries in the event of temporary failures
Set up automatic retry systems with intelligent intervals to handle temporary failures. Remember that many platforms set a maximum of 10 requests per second, and exceeding this limit can result in temporary or permanent blocks. Asynchronous APIs are optimized to process large volumes of numbers in parallel, returning results via HTTP callbacks.
MNP verification integration as an add-on
MNP (Mobile Number Portability) verification works perfectly alongside the HLR lookup. When a number has been ported, this verification provides you with information about both the original and current carrier, optimizing message routing and reducing costs.
Using geo-redundant HLR lookup APIs
Geo-redundant APIs ensure continuous availability in the event of regional failures. You can choose between two main types: synchronous for individual checks and asynchronous for bulk processes. The right implementation can be completed in less than three minutes, enabling programmatic queries from any application or system.
When to Consider Alternatives to Traditional HLR
There are specific situations where the traditional hlr lookup will not give you the results you need. We recommend that you evaluate these circumstances before making a decision.
Legal or privacy limitations in certain countries
HLR verification faces significant restrictions due to privacy regulations. Many carriers block sensitive information such as roaming status or location to comply with consumer protection legislations. Article 45 of the GDPR limits transfers of personal data to countries without an “Adequacy Decision”, directly affecting the operation of these services.
Use cases where HLR is not enough (fraud, onboarding)
Do you work on digital onboarding processes? Especially in regulated industries with KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements, you’re going to need additional tools. For projects in the financial sector, the HLR alone will not help you prevent sophisticated fraud.
Use of proprietary validators or silent SMS verification
Proprietary validators offer you alternatives when access to the HLR is restricted. Remember to be careful with silent SMS, as they can be used both for validation and for attacks that monitor geolocation without any notification.
Comparison between HLR lookup and bulk HLR lookup
The basic Lookup service is free and verifies correct formats by classifying numbers as mobile or landline. On the other hand, bulk HLR allows you to process massive volumes using CSV upload or API integration, making it the ideal choice when handling large databases.
Conclusion
HLR verification is undoubtedly a key tool for optimizing your mobile communication campaigns. Throughout this article, you’ve discovered that the main problems are often caused by formatting errors, carrier coverage limitations, SS7 network restrictions, difficulties with virtual numbers, and complications during portability.
Now you know how to interpret the most important parameters such as is_reachable, line_type and carrier, as well as understand the relevance of MCC/MNC codes to identify specific mobile networks. You’ve also learned what to do when “unknown” answers or technical errors appear during your checks.
To solve these technical hurdles, you can apply the solutions that really work: use multiple vendors at the same time, pre-validate formats with specialized libraries, set up automatic retries, integrate MNP verification, and leverage geo-redundant APIs. Verifyemails has developed a solution that allows you to validate phone numbers reliably without coverage limitations.
Remember that there are situations where traditional HLR is not enough, especially when you face legal privacy limitations, cases of fraud, or onboarding processes that need more robust verification. For these scenarios, proprietary validators or specialized services may be the perfect solution.
The choice between basic or bulk HLR lookup will depend on the volume of numbers you need to verify and your specific integration requirements. By putting these technical recommendations into practice, you will significantly improve the validation rate of your phone numbers, optimize resources and achieve much more effective communications with your customers.
Key Points HLR Verification
HLR verification failures have specific technical solutions that can significantly improve your validation rate and optimize your mobile communication campaigns.
• E.164 formatting errors are the main cause: Use libraries such as libphonenumber to validate numbers before HLR queries and avoid special characters or incorrect prefixes.
• Deploy multiple vendors simultaneously: HLR vendor redundancy increases global coverage and ensures responses even when a vendor is time-bound.
• Set up intelligent automatic retries: Respect the limit of 10 requests per second and schedule retries to overcome temporary failures in SS7 networks.
• Complements HLR with MNP verification: Mobile number portability provides current and original carrier information, optimizing routing and reducing costs.
• Consider alternatives when HLR is not enough: For fraud, KYC onboarding, or legal privacy restrictions, use proprietary validators or specialized services.
The key to success is to combine these technical strategies according to your specific needs, creating a robust system that maximizes validation accuracy while minimizing operational costs.
FAQs
Q1. What is an HLR check and why is it important? An HLR (Home Location Register) check is a process that queries the central database of mobile operators to determine the actual status of a phone number. It is important because it allows you to optimize SMS marketing campaigns and reduce costs by targeting only active and available numbers.
Q2. What are the main causes of failures in HLR verification? The main causes include format errors in international numbers (E.164), limited mobile operator coverage, access restrictions to SS7 networks, problems with virtual or temporary numbers, and complications during number portability (MNP).
Q3. How can I improve the validation rate on my HLR checks? To improve the validation rate, you can use multiple HLR lookup providers simultaneously, pre-validate the format of numbers with libraries such as libphonenumber, implement automatic retries in the event of temporary failures, integrate MNP verification as an add-on, and use geo-redundant APIs.
Q4. What do the is_reachable, line_type, and carrier parameters mean in the HLR lookup results? Is_reachable indicates whether the number is active and available, line_type identifies the type of line (mobile, landline, etc.), and carrier displays the current operator of the number. These parameters are essential for correctly interpreting the results of the HLR verification.
Q5. When should I consider alternatives to traditional HLR? You should consider alternatives to traditional HLR in cases of legal or privacy limitations in certain countries, fraud situations or onboarding processes that require more robust verification, or when you need to validate large volumes of numbers. In these cases, options such as proprietary validators or specialized services may be more suitable.