In this article, you’ll learn how to identify the most common phishing emails and the techniques cybercriminals use to trick you. We’ll show you the red flags you should be aware of and what to do if you receive a suspicious message in your inbox.
Key Points
Protect yourself from phishing by knowing the warning signs and applying preventive measures that can save your personal and financial information.
• Identify key signs: Suspicious addresses, grammatical errors, fake urgency, and requests for personal data are clear indicators of phishing.
• Never interact with suspicious content: Don’t click on links or download dubious email files; Always verify directly with the official entity.
• Enable two-step verification: This extra measure protects your accounts even if cybercriminals get your password.
• Stay up-to-date and trained: Ongoing education on new phishing techniques is your best defense against these ever-evolving threats.
• Report fraud attempts: Report suspicious emails to your supplier and impersonated companies to help prevent future attacks.
Remember that phishing accounts for 15% of all data breaches and almost 30% of people open fraudulent emails. Your personal vigilance remains the most effective first line of defense against these attacks.
What is phishing and why should you know about this threat?
Image Source: Cloudflare
Phishing is a technique used by cybercriminals to steal sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or bank details. Attackers pose as legitimate companies and send fraudulent messages to trick you. This threat has become the most effective method of cybercrime because it exploits something very human: trust.
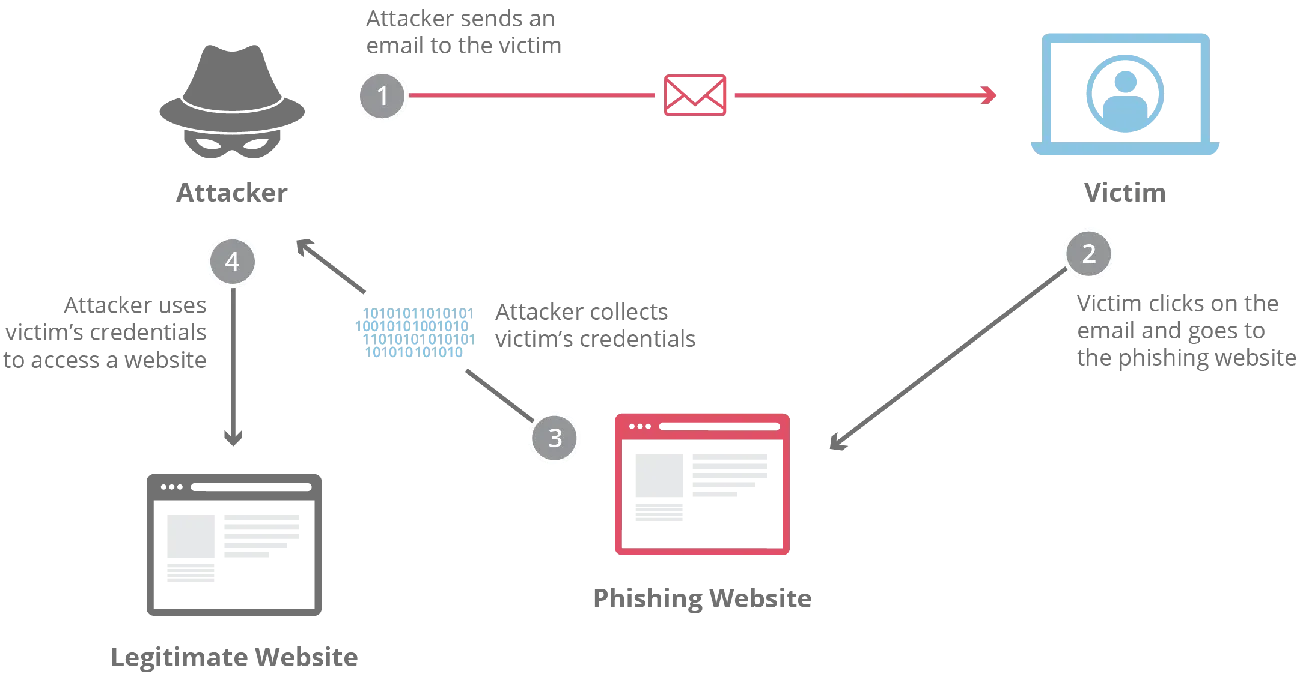
How do attackers execute phishing step by step?
Cybercriminals follow a systematic process to deceive their victims. Here’s how it works:
Step 1: The attacker defines their targets and selects potential victims.
Step 2: Do some preliminary research on yourself or your business.
Step 3: Identify and research specific targets in detail.
Step 4: Write the message using social engineering techniques.
Step 5: He sends the email pretending to be a trusted entity.
The success of these attacks lies in creating a false sense of urgency. Scammers use emotional manipulation techniques to get you to act without thinking. A fact that may surprise you: phishing accounts for 15% of all data breaches, with an average cost to organizations of $4.88 million.
How is phishing different from other cyberattacks?
While other attacks target technical vulnerabilities, phishing exploits human error. They pressure you to make rash decisions. Unlike ransomware that hijacks systems, or DDoS attacks that crash services, phishing specifically seeks to steal your personal or financial information.
Here’s a troubling fact: Nearly 30% of people open the fraudulent emails they receive, and another 13% click on the malicious link. This shows why it’s so important that you learn how to identify them.
Types of phishing you should know about
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with these specific terms to better protect yourself:
Vishing: Combination of “voice” and “phishing”. Scammers call you posing as employees of your bank to get SMS keys or digital tokens.
Smishing: Phishing via SMS messages. You receive texts from supposed banks asking you to call fake numbers or follow fraudulent links.
Pharming: It redirects you to fake pages via pop-ups, without the need to click on links.
Whaling: Attacks targeting high-level executives, using personalized emails on urgent corporate matters.
Remember that these methods are constantly evolving. Attackers use technologies such as artificial intelligence to create more compelling and harder-to-detect messages.
7 Signs That Help You Identify Phishing Emails
How can you tell if that email you just received is legitimate or a scam? Cybercriminals make mistakes that you can easily spot if you know what to look for. Here are seven key indicators to check before interacting with any message.
Step 1: Check the sender’s address
Carefully examine the domain where the mail comes from. Scam addresses include additional characters or minor modifications. Instead of “amazon.com” you might find “amaz0n-secure.com” or “amazon-verificacion.com.”
Remember to hover over the sender’s address without clicking. If the address that appears is different from the one shown, it is a clear red flag.
Step 2: Look for errors in the text
Professional companies carefully review their communications. If you find obvious spelling mistakes or grammatical errors, be wary of the message. Scammers sometimes deliberately include these errors to filter out more vulnerable people.
Step 3: Analyze the subject of the email
“Password verification required immediately” is the most commonly used subject in phishing attacks, with 43% effectiveness. Scammers use alarming phrases to create artificial urgency. Always be wary of messages that demand immediate action or threaten to block your account.
Step 4: Identify requests for personal information
No legitimate company will ask you for passwords, credit card numbers, or security codes via email. Banks and commercial entities use secure channels to request this type of information. If you receive such a request, it is phishing.
Step 5: Evaluate suspicious offers
Unexpected prizes, unsolicited tax refunds, or windfall wins are typical signs of scams. If you have not participated in any giveaway or have not requested information about those services, it is very likely that it is a scam.
Step 6: Don’t interact with links or files
Before clicking on any link, hover over it to see the actual URL. Executable (.EXE) files, Office documents, and PDFs can contain malware. If you didn’t expect to receive these files, don’t open them.
Step 7: Verify contact information
Legitimate emails include complete company data: physical addresses, phone numbers, and links to official websites. The absence of detailed contact information is a warning sign that you shouldn’t ignore.
We recommend applying these seven steps every time you receive a suspicious email. The combination of several indicators significantly increases the likelihood that it is a phishing attempt.
What to do if you receive a suspicious email
Have you identified a suspicious message in your inbox? Doing the right thing can save your account and protect your personal data. Below, we will show you the steps you should take to minimize the risks.
Step 1: Verify the sender’s details
Carefully examine the sender’s information before taking any action. In most email clients, you can access the full message headers by selecting options such as “View Message Source” or “Properties.”
We recommend using tools like MessageHeader to interpret this technical data in a simple way. This will allow you to check if the IP address actually matches the organization it claims to be.
Step 2: Don’t interact with the message content
Remember that if you suspect an email is fraudulent, you should never click on any links or download attachments. Even if the link looks legitimate, it could contain dangerous malware for your device.
If you need to verify any information with the entity, go directly to its official website by typing the URL into your browser. Never use the links in the suspicious email.
Step 3: Report the phishing attempt
It is essential to report these attempts to protect other users. The process is simple:
- In Gmail: Select the message, tap the three dots button, then choose “Report phishing”
- In Outlook: Select the email, then “Report” and finally “Phishing”
If the message impersonates a recognized company, we recommend that you contact them directly to alert them about the fraud attempt.
Step 4: Act quickly if you accidentally clicked
If you accidentally interacted with the suspicious email, immediately disconnect your device from the internet. This will prevent the malware from spreading or sending your data to cybercriminals.
Then, run a full scan with your antivirus software. We recommend changing the passwords for your important accounts from another secure device, especially if you’ve entered credentials on suspicious sites.
Tools and best practices to prevent phishing
To protect your accounts against phishing attacks , we recommend combining technological tools with good preventive practices. Implementing multiple layers of security significantly reduces risks to your data.
Enable spam filters and two-step verification
Two-step verification adds an extra layer of security even if your password is compromised. When you log in, you’ll need both your password and a second verification step: a code sent to your phone or generated by an authenticator app.
This protection is especially effective against phishing. Even if cybercriminals get your password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second factor of authentication.
Use anti-malware and antivirus software
We recommend anti-malware software such as Microsoft Defender, Malwarebytes, or Bitdefender for real-time protection against digital threats. These tools actively scan emails and attachments for malicious content before it can harm your system.
In addition, they include specific anti-phishing features that automatically identify and block fraudulent websites.
Continuous staff training
Regular cybersecurity training significantly reduces the risk of successful attacks. Companies can implement awareness programs that include controlled phishing simulations to train employees.
According to recent studies, 86% of employees click on phishing links without proper training. Remember that continuing education is your best defense.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols for enterprises
If you run a business, we recommend implementing these three email authentication protocols. They help verify that the messages are actually coming from the domain they claim to represent:
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Specifies which servers are authorized to send mail from your domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Add a verifiable digital signature to your emails.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication): Sets policies on what to do with emails that fail the above checks.
Implementing these protocols is simple and will provide you with additional protection against domain spoofing.
Protecting your data from phishing is in your hands
Phishing attacks will continue to be a real threat to your personal accounts and financial data. However, you now have the tools you need to identify these fraud attempts before they cause harm.
Remember that your personal vigilance is the most effective first line of defense. Spam and antivirus filters help, but your ability to recognize suspicious addresses, grammatical errors, and urgent requests makes all the difference.
We recommend turning on two-step verification on all your important accounts. This extra measure protects your information even if cybercriminals get their hands on your password. It’s a time investment that can save you from losing access to your accounts or suffering financial losses.
If you receive a suspicious email, don’t panic. Follow the steps you’ve learned: verify the sender, don’t click on dubious links, and report the incident to your email provider.
Education about these threats is an ongoing process. Cybercriminals are constantly perfecting their techniques, but your knowledge can also grow. Stay informed about new phishing modalities and share this information with family and coworkers.
Validating email addresses using tools such as email checker helps identify wrong addresses and invalid emails that can be used as senders of attacks.
If you have any questions about your email security or need help implementing preventative measures, our team will be happy to help. The protection of your personal data is a shared responsibility.
FAQs
Q1. What are the most common signs of a phishing email?
The most common signs include suspicious email addresses, spelling and grammatical errors, unwarranted sense of urgency, requests for personal information, and malicious links or attachments.
Q2. How can I check if an email is legitimate or a phishing attempt?
Carefully check the sender’s address, don’t click on suspicious links, be wary of urgent requests for personal information, and check directly with the supposedly sender company through their official channels.
Q3. What should I do if I think I have received a phishing email?
Don’t interact with the content of the email, report the message to your email provider, alert the impersonated company if applicable, and run an antivirus scan if you’ve clicked on any links or downloaded files.
Q4. What security measures can I implement to protect myself against phishing?
Enable two-step verification on your accounts, use up-to-date anti-malware software, stay informed about the latest phishing techniques, and be wary of unsolicited communications that ask for personal or financial information.
Q5. Why is phishing considered so dangerous compared to other types of cyberattacks?
Phishing is particularly dangerous because it exploits human trust and errors in judgment, can evade many technical security measures, and often results in the direct theft of sensitive or financial information, causing significant damage to individuals and organizations.