Have you noticed that some of your email marketing campaigns just don’t make it to your subscribers’ inboxes? Feedback loops may be exactly what you need to fix this problem. These systems allow you to receive direct reports when your recipients mark your emails as spam.
Feedback loops have become critical as email marketing has evolved. You can now access detailed data on successful deliveries, opens, clicks, spam reports, and unsubscribes. When you remove complaining subscribers from your emails, you keep your complaint rate under control and significantly improve your chances of reaching inboxes.
Here’s the key point: mail providers rate the reputation of your sending IP addresses. A high number of complaints damages this reputation, which increases the risk of your emails being blocked or marked as spam. That’s why implementing a feedback loop correctly protects your reputation as a sender and improves your deliverability.
In this article, you’ll learn exactly what feedback loops are, how to set them up step-by-step, and how they can double your open rate. We’ll show you the direct impact they have on the deliverability of your emails and how to implement them effectively in your campaigns.
What is a Feedback Loop and why does it matter in email marketing?
Feedback loops are services offered by email providers to keep you informed when your messages are marked as spam. Think of them as an early warning system that alerts you immediately when something goes wrong with your campaigns.
These systems are crucial for any business that sends mass emails. They allow you to quickly identify subscribers who complain about your messages and remove them from your future lists. Plus, you can spot specific issues in your campaigns before they damage your sender reputation.
The importance of feedback loops lies in their ability to protect your email marketing investment. When you keep your complaint rate in check, email providers trust your mailings more and allow them to reach inboxes instead of being filtered as spam.
What is a Feedback Loop and why does it matter in email marketing?
Technical definition of feedback loop (FBL)
A feedback loop (FBL) is a service that mailbox providers (ISPs) offer to notify you when your messages are marked as spam by recipients. The process works simply: when a recipient marks your email as spam, the ISP automatically generates a complaint report and sends it to you, as long as you are registered in their FBL system.
These reports use the Abuse Notification Form (ARF), which includes three essential parts: human-readable information, machine-actionable data, and a copy of the original message that generated the complaint. This way, you can identify exactly what type of content is causing problems with your subscribers.
Why are feedback loops important in mass campaigns?
If you’re sending large volumes of emails, feedback loops allow you to quickly identify dissatisfied users and take corrective action. Key benefits include:
- Protection of your domain reputation and IP, preventing complaints from affecting both promotional campaigns and transactional emails
- Reducing the spam rate and improving your sender score
- Content optimization based on real user feedback
- Early identification of problematic campaigns that don’t connect with your audience
Remember that implementing an FBL requires specific technical configuration and understanding of data analysis tools.
Difference Between Short and Long Feedback Loop
ISPs handle two types of feedback loops depending on the detail of information they provide:
Short (individual) feedback loops: Providers like Yahoo! send detailed individual reports that include the recipient’s email address and the entire message that caused the complaint. These allow you to act immediately on specific cases.
Long (aggregated) feedback loops: Gmail uses a different approach, providing aggregated reports that don’t reveal specific addresses but offer collective data about campaigns, products, or regions. These require deeper analysis to identify overall trends.
To sign up for FBL programs, you must meet specific requirements: be a high-volume sender and prove ownership of, or have administrative rights to, the IP address and domain.
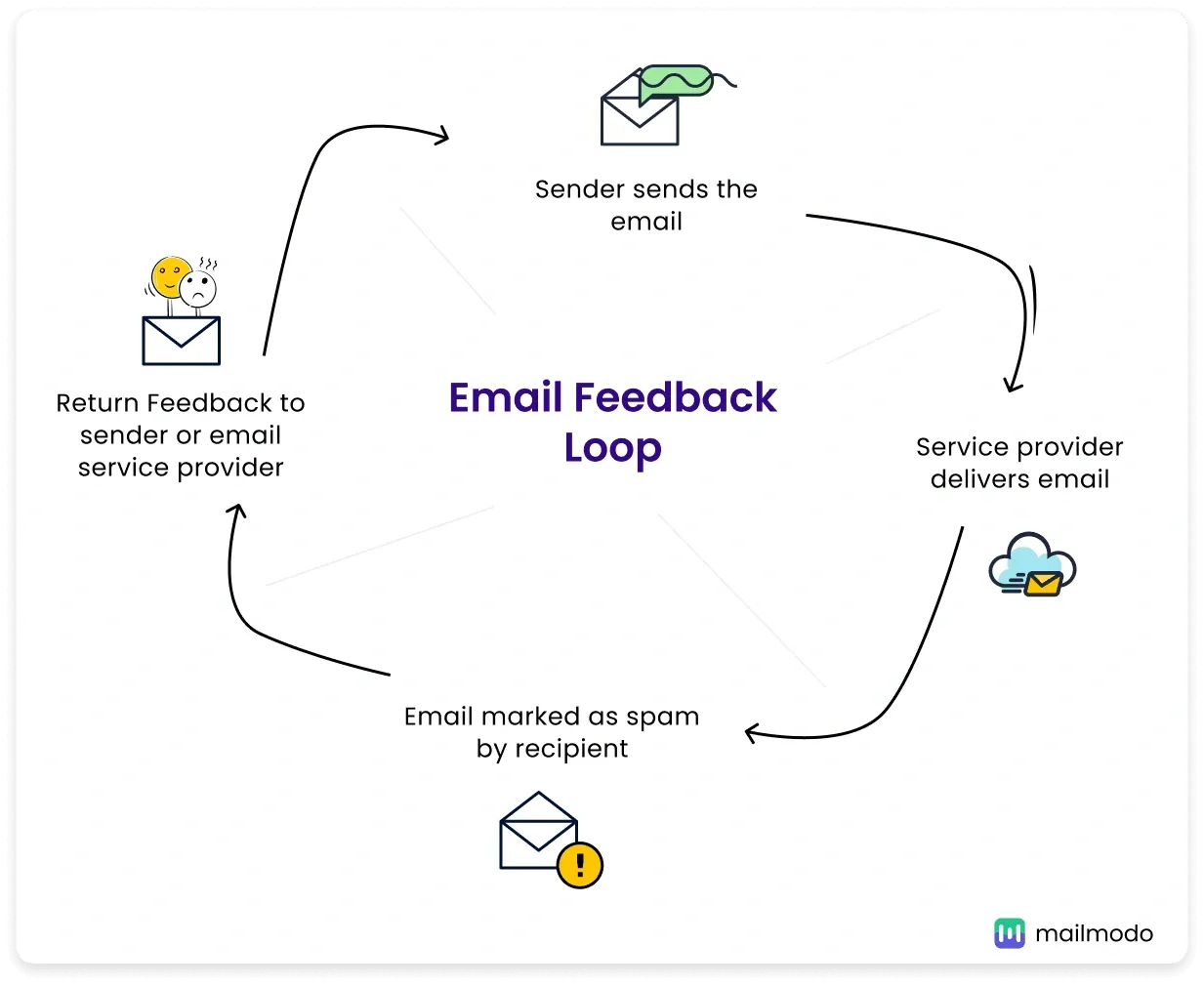
How a Feedback Loop Works in Practice
Image Source: Mailmodo
Here’s how this process works step by step. When a subscriber receives your email and chooses to mark it as spam, it automatically triggers a chain of events that can protect your reputation as a sender.
The process begins when the recipient clicks on the “Mark as spam” button in their email client. At that point, the internet service provider (ISP) generates a complaint report that includes details about the flagged message. If you are registered in that ISP’s feedback loop program, you will receive an automatic notification about this complaint.
This notification allows you to quickly identify which subscribers are dissatisfied with your communications. With this information, you can automatically remove those addresses from your future campaigns, preventing additional mailings that could damage your reputation.
Remember that feedback loops work as an early warning system. They help you spot problems in your campaigns before they become a major damage to your deliverability.
How a Feedback Loop Works in Practice
User complaint process and submitter notification
The process starts very simply. A recipient marks your email as spam using the corresponding button in their email client. Immediately, the messaging service provider generates a feedback report and sends it to you if you are registered in their FBL program.
This system allows you to act quickly. Whenever you receive a complaint notification, you can automatically remove that address from your future campaigns. This keeps your database clean and protects your reputation as a sender.
Remember that in order to receive these reports, you must first register for the FBL programs of the providers your audience uses. Once configured, the process works automatically.
FBL Types: Individual vs Aggregate
Feedback loops work in two different ways depending on the provider:
Individual FBLs: Providers like Yahoo! send you detailed reports in ARF (Abuse Reporting Format) format. These reports include the exact address of the recipient who complained, the body of the original message, and the abuse notification. With this information, you can specifically identify which users are dissatisfied.
FBL Added: Gmail handles complaints differently. It doesn’t provide you with individual addresses, but aggregated data about specific campaigns, products, or regions. This information helps you identify general trends rather than individual cases.
Providers that offer FBL: Yahoo, Outlook, Gmail
Each major provider has its own registration requirements and processes:
Yahoo!: You need to fill out a request form for your Complaint Feedback Loop (CFL). You must include your DKIM selector, as it only supports reporting for DKIM-authenticated domains.
Outlook: Use its JMRP (Junk Mail Reporting Program) program. You can sign up directly for complaint notifications.
Gmail: It doesn’t offer a traditional FBL. Instead, it uses a system based on Postmaster Tools.
Feedback-ID header in Gmail and its use in Postmaster Tools
Gmail requires a specific approach. You should add the Feedback-ID header to your emails in this format:
Feedback-ID: a:b:c:SenderId
Where:
- a, b, c: Optional identifiers for campaign, customer, or other parameters
- SenderId: Required unique identifier (5-15 characters)
This header allows Gmail to group your emails and provide aggregated statistics in Postmaster Tools. To work properly, your emails must be authenticated with DKIM from a verified domain. In addition, your sending IPs must be published in the SPF records of the signing domain.
Direct impact of FBL on deliverability and open rate
Direct impact of FBL on deliverability and open rate
Reduced complaints and improved domain reputation
Feedback loops act as an early warning system that allows you to respond quickly to your subscribers’ complaints. Mail providers assign a reputation score to your sending IP addresses, and maintaining a low number of complaints protects this rating.
When you implement FBLs correctly, you protect not only your promotional campaigns but also your critical transactional emails like order confirmations, invoices, and security alerts. Frequent complaints can affect the delivery of all your business communication, not just marketing.
Targeting and content optimization
Data from feedback loops reveals specific patterns about what type of content generates rejection from your subscribers. If you notice that a particular campaign receives a lot of complaints, this indicates problems in the segmentation or in the message itself.
While not all providers offer individual data, you can analyze complaint rates by:
- Campaign type (promotional, informational, transactional)
- Demographic Segment
- Geographical location
- Sending frequency
This information allows you to adjust your content strategy to make it more relevant and reduce rejection from your subscribers.
Automatic Subscriber List Cleaning
A fundamental rule in email marketing is to keep lists clean and up-to-date. Feedback loops allow you to automatically identify dissatisfied subscribers and exclude them from future submissions. This debugging process significantly reduces bounces and spam complaints.
To streamline this process, we recommend using the API to validate email addresses that automate the cleanup of your databases.
How FBLs Help Double Open Rate
A curated list automatically improves your metrics without the need to modify the content of your emails. By only sending to engaged subscribers, your open rates naturally increase.
Data shows that automated emails based on specific behaviors achieve up to 199% higher open rates than traditional mass mailings. When you remove recipients who mark your messages as spam, you can:
- Improve your reputation with mail servers
- Reduce the bounce rate below 15.8%
- Increase the relevance of your communications
- Strengthen overall engagement with your brand
Remember to validate email addresses regularly to maintain these benefits in the long run.
Direct impact of FBL on deliverability and open rate
Reduced complaints and improved domain reputation
Feedback loops allow you to act quickly when you receive complaints from your subscribers. Remember that email providers continually rate your sending IP addresses, and a high number of complaints negatively impacts this rating, which can result in blocks or classification as spam.
We recommend implementing FBLs correctly because they protect all your types of mail: from promotional campaigns to transactional emails such as confirmations, invoices, and alerts. Frequent complaints do not discriminate between types of mail; affect all your business communication.
Targeting and content optimization
Do you notice that certain campaigns generate more complaints than others? FBLs help you identify exactly what content or targeting is failing. While not all providers give you individual data, you can analyze patterns by campaign type, demographics, or location.
Analyzing these patterns allows you to detect which campaigns or content generate the most rejection. Once you identify these pain points, you can adjust your communications to make them more relevant and improve your subscribers’ experience.
Automatic Subscriber List Cleaning
Maintaining a clean database is critical to successful email marketing. Feedback loops allow you to automatically identify dissatisfied subscribers and exclude them from future submissions [6]. This debugging process significantly reduces bounces and spam complaints, ensuring a delivery rate close to 99%.
If you’re going to use list cleaning services on a regular basis, we recommend using tools like the Email Address Validation API to fully automate this process.
How FBLs Help Double Open Rate
A curated list automatically improves your metrics. By only sending to subscribers who actually interact with your emails, open rates naturally increase. Automated emails based on specific behaviors achieve up to 199% higher open rates than mass mailings.
When you remove recipients who mark your messages as spam, you get these benefits:
- Improve your reputation with mail servers
- You reduce the bounce rate below 15.8%
- You increase the relevance of your communications
- Improve overall engagement with your brand
To maintain these results, remember to verify email addresses regularly and adjust your campaigns based on the feedback you receive.
Step-by-step guide to implementing an effective Feedback Loop
Now that you know the impact of feedback loops on your campaigns, it’s time to implement them correctly. The setup may seem technical at first, but following these steps will get you results from day one.
Remember that setting up an effective feedback loop requires meeting certain technical requirements and signing up for the programs of the main providers. Once the process is complete, you will see how your deliverability improves and engagement with your subscribers increases.
Step-by-step guide to implementing an effective Feedback Loop
Technical requirements: SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and rDNS
Before setting up your feedback loop, you need to set up the basic authentication protocols. SPF authorizes which servers can send mail from your domain, DKIM adds a digital signature that verifies the authenticity of your messages, and DMARC defines policies when these checks fail.
Since 2024, these protocols are mandatory for mass mailings to Gmail and Yahoo. You should also set up reverse DNS records (rDNS) so that servers can verify that your IP is authorized to send from your domain.
Registration in FBL programs of ISPs
Once you’ve set up authentication, you can proceed with the registration in the feedback loop programs:
Step 1: Yahoo Mail
Complete the request form for your Complaint Feedback Loop (CFL). You’ll need to provide your DKIM selector, as Yahoo only accepts reports from successfully authenticated domains.
Step 2: Outlook
Sign up for Microsoft’s Spam Reporting Program (JMRP). This process is more straightforward than Yahoo and will allow you to receive complaint reports from Outlook users.
Step 3: Gmail
Although Gmail doesn’t offer a traditional FBL, it uses Postmaster Tools to monitor the performance of your sends. Set up your account and add the Feedback-ID header to your emails.
For all of these records, you’ll need to set up a specific address as a abuse@tudominio.com or postmaster@tudominio.com to receive the reports.
Automation with ESPs like Mailchimp or Mailtrap
If you use email service providers, many already integrate feedback loop management. Mailchimp, for example, automatically handles complaints and removes problematic subscribers from your future lists.
Mailtrap offers a more advanced solution: it connects directly to FBLs from major providers and automatically updates your suppression lists when someone marks your emails as spam.
Using tools like the Suppression List API
To fully automate the opt-out process, we recommend using a validate emails api. This tool allows you to manage suppression lists using REST calls.
For example, to add a problematic email to your exclusion list:
PUT /api/v1/suppression-list/{recipient_email}
The API also allows you to check the suppression status before sending campaigns, ensuring that you don’t contact users who have previously filed complaints.
📌 See the Email Validation API documentation
Feedback Loops: Your Next Step Towards Better Campaigns
You’ve seen how feedback loops can completely change the results of your email marketing campaigns. These systems give you direct access to valuable information about what your subscribers really think of your emails.
The benefits are clear: you reduce complaints, protect your reputation as a sender, and significantly improve your open rates. When you implement feedback loops correctly, you can double your open rate simply by keeping lists cleaner and more relevant.
Does the technical setup seem complicated to you? Do not worry. While you need to set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, many email marketing platforms already include these features. Once set up, feedback loops work automatically to maintain your reputation.
Remember that keeping clean lists is critical to success. You can validate email addresses regularly to ensure that your campaigns reach real and engaged recipients.
Feedback loops aren’t just technical tools – they’re your direct connection to what your subscribers really want. Use this information to create more relevant campaigns, improve your targeting, and deliver content that really interests your audience.
The investment in implementing feedback loops is recouped from your first improved campaign. Getting started is easier than it seems, and the results speak for themselves.
If you have any questions about how to implement feedback loops or need help with validating your mailing lists, our team will be happy to help.
FAQs
Q1. What is a feedback loop in email marketing?
A feedback loop is a system that allows internet service providers to notify senders when their emails are marked as spam by recipients. This helps improve deliverability and protect sender reputation.
Q2. How do feedback loops work in practice?
When a user marks an email as spam, the email provider generates a report that is sent to the sender registered in its feedback loop program. This allows the sender to quickly identify and respond to complaints, keeping their database clean.
Q3. What impact do feedback loops have on open rate?
Feedback loops can help double the open rate by allowing for the removal of inactive or complaining subscribers, improving sender reputation and increasing the relevance of communications to the remaining recipients.
Q4. What technical requirements are necessary to implement a feedback loop?
To implement an effective feedback loop, you need to correctly configure authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, as well as configure reverse DNS records (rDNS) to verify sending authorization from your domain.
Q5. How can I sign up for feedback loop programs from major providers?
To sign up for feedback loop programs, you must meet the technical requirements and then enroll in each provider’s specific programs. For example, Yahoo requires you to fill out a form and provide your DKIM selector, while Outlook offers its Junk Email Reporting Program (JMRP).